Which is the right choice, BYOD or COPE?

What is BYOD and COPE?
|
|
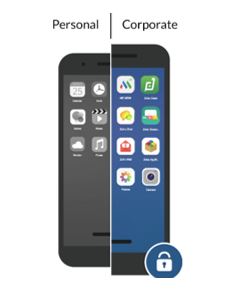
BOYD (Bring Your Own Device) is when you enrol your personal phone into UEM (Unified Endpoint Management) once enrolled it will create a container that creates a work profile, letting you access company resources. COPE (corporate-owned, personally enabled) turns a corporate owned device into two-sided phone, one for personal use and other for work only.
|
How are they the same?
They both can have a work side and personal side, both have MAM (mobile application management), IT staff can control work resources with policies, device security and both options allow for centralised management of the devices, Compliance and policy implementation to protect and control the work side of the device. The IT admin can require a password for the work profile, disable sharing between private side and work side and even stop screen shots from happening.
Advantages and Disadvantages of BYOD?
Advantages:
- Cost savings: Companies can save on hardware costs since employees use their own devices.
- Increased employee satisfaction: Employees are often more comfortable and productive using familiar devices.
- Reduced training: Minimal training is required as employees are already familiar with their devices.
- Employee device choice: Employees get to use the devices they like.
Disadvantages:
- Security risks: Companies face certain challenges in controlling and securing a diverse device fleet, if not implemented correctly this can increase the risk of a data breach.
- Data privacy concerns: It is important to have effective policies and strategies in place to handle the distinction between personal and corporate data which if not properly managed can lead to privacy issues.
- IT support challenges: Supporting a wide range of devices and operating systems can be complex without the right UEM solution.
- Data loss potential: If a personal device is lost or stolen the company will require the correct policies and processes to be in place or corporate data may be compromised.
- Compatibility issues: different devices and operating systems can cause issues with company applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages of COPE (Corporate-owned, Personally Enabled)?
Advantages:
- Enhanced security: Companies have greater control over device security, allowing for stricter policies and data protection.
- Improved data control: Companies can more easily manage and protect sensitive corporate data.
- Simplified IT support: Standardized devices deployments make IT support and troubleshooting easier.
- Clear separation of data: using containerization, business and personal data can be kept separate.
- Control over updates: Companies can control operating system and application updates more efficiently.
Disadvantages:
- Higher costs: Companies bear the expense of purchasing and maintaining the device fleet.
- Reduced employee flexibility: Employees will generally have limited device choices.
- Privacy concerns: employees may be worried about company monitoring of their device usage, although this can be alleviated by proper information sharing and training.
- Logistics: It may take more company resources to properly deploy a fully managed COPE strategy.
Conclusion
The best approach depends on the organization's specific needs, security requirements, and budget. Organisations in highly regulated industries (e.g., finance, healthcare) may prefer COPE for stricter security. Smaller businesses with limited budgets may opt for BYOD. Both solutions can be secured and compliant however the methods of deployment can be very different.